Rat External and Fresh Visceral
EXAMINATION OF FETAL SPECIMENS - OVERVIEW
This training web has been designed as a programme of training and assessment to support the Society of Biology's International Register of Fetal Morphologists. It provides learning material that will complement practical training received 'in house'.
It is preferable that the candidate attends the 'Introduction to fetal morphology' presentation prior to, or shortly after, commencement of practical training.
To conduct fetal examinations adequately, it is important to have a clear idea of the normal anatomy and of how to describe variations from the norm. Apart from basic knowledge of the relevant fetal anatomy, some broader background or training in embryological development will also be very valuable.
The training web presents important topics as 'learning objectives' and uses images and diagrams to demonstrate current popular practices and conventions. The candidate should, however, always refer to their own laboratories Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and user guides and use this training web alongside their own material.
The candidates understanding of the learning objectives can be assessed using the 'learning outcome' exercises provided.
The material contained in this web provides training and guidance relevant to RAT FRESH EXTERNAL AND VISCERAL EXAMINATION.
RAT FRESH EXTERNAL AND VISCERAL EXAMINATION - INTRODUCTION
Why are fetuses examined?
The aim of regulatory reproductive toxicity studies is to reveal any effect of an active substance on mammalian reproduction. In one of the studies designed to achieve this aim pregnant animals are treated during the period of embryonic/fetal development.
Current International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) guidelines require that these embryofetal development studies are performed in 2 laboratory animal species (one rodent and one non-rodent), and that fetuses from the treated dams are examined for developmental and structural abnormalities, by soft tissue and skeletal examination techniques.
The rat is commonly chosen as the rodent species and the current ICH guidelines, referred to above, specify that "a minimum of 50% rat fetuses should be examined for visceral alterations, regardless of the technique used."
Why is technique used?
There is a regulatory requirement to examine the external surface and internal structures of the thorax and abdomen in rat specimens.
Advantages of the fresh examination technique:
Facilitates examination of external surfaces and internal structures, as required by regulatory guidelines, for structural abnormalities and developmental delay.
As the technique is performed on fresh fetuses, examination of the specimens is performed in a short time frame , and therefore examination results are available quickly.
The technique allows:
retention of tissue for future reference/further examination.
further investigations are possible, for histopathological confirmation of lesion.
Tissues remain flexible, the patency of blood vessels and other tubular structures is determined relatively easily.
The 3D appearance of the specimen makes understanding of the spatial relationship of different structures with each other relatively easy.
Training to examine fresh specimens
Ideally the trainee should be provided with a training plan and the date of any training received should be recorded. Regular review of the trainee's progress is essential.
SOPs and user guides should be made available as training materials. These should be referred to, along with any other relevant materials, such as this training web, during training. Adherence to Good Laboratory Practices should be evident at all times.
Initial teaching sessions are ideally organised on a one-to-one basis, interspersed with time allowed for the trainee to practice, consolidating what has been learned. Wherever possible, the use of materials from studies that have already been evaluated will avoid time pressures at this stage.
Once this initial phase has been completed, training can then be continued 'on-study' with close supervision by experienced examiners. Initially, training should include 100% review of the examinations performed by the trainee, gradually reducing as competency is acquired. The time taken to achieve competency will naturally depend on work throughput, as much as on the aptitude of the trainee, and it might be necessary to revert to more exhaustive checking if checking/review reveals an increasing level of inaccuracy or inconsistency. It is expected that the trainee would have 18 months experience in the technique, and have evaluated a minimum of 500 litters before they are be considered fully competent.
It is recommended that all structures listed on the The International Register of Fetal Morphologists (IRFM) Expected Minimum Structure List for Fetal Morphology Examinations document be examined and that the Fresh rat external and visceral examination - key structures and notes document be used as a reference.
Learning objectives:
- Familiarise yourself with your training objectives
- Review 'in house' training material
- Review UK IRDG recommended minimum requirements for fetal examinations document
Requirements for examination
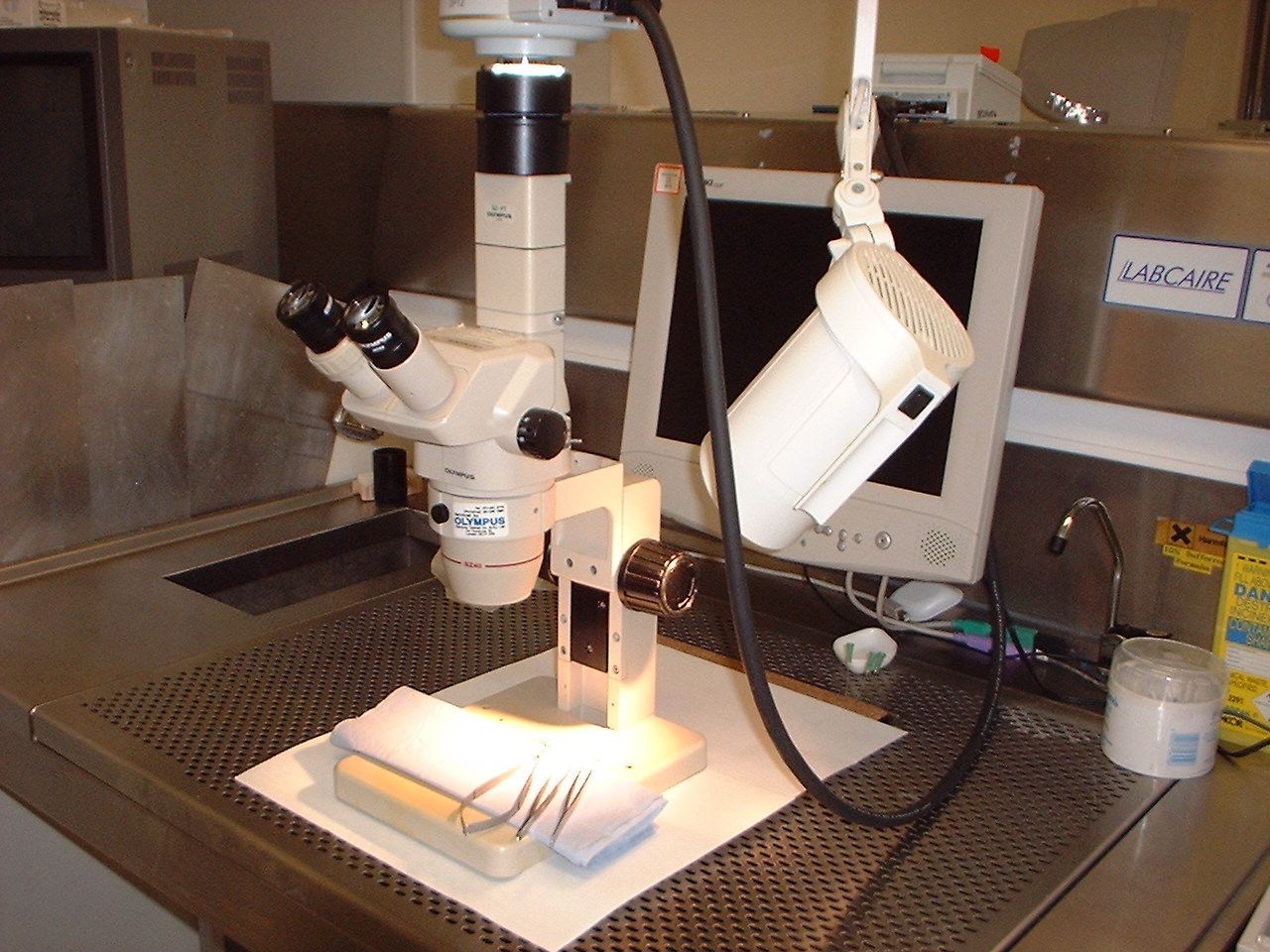
For the examination of fresh rat specimens, low-power magnification is recommended. A good light source is also essential with the specimen being illuminated from above. The setup pictured below demonstrates illumination from above using a flexible overhead light.
The specimen can be moved and manipulated using fingers and forceps, however, the examiner should find what is comfortable for them whilst allowing free movement.
Since there is no absolute and wholly objective standard against which to evaluate specimens, every effort should be made to assess the anatomy in exactly the same way for every fetus, applying identical criteria to distinguish 'normal' from 'abnormal'. It is recommended that measures to ensure a consistent approach be built in to any laboratory's work practice. Working methodically should increase the consistency of examination and limit the likelihood of omissions. Whether all examiners in a laboratory should be required to follow the same routine or be allowed to develop their own is a matter for individual preference, but some degree of consistency is desirable.
Remember:
Magnification
Binocular microscope, x6 minimum
Light source
Flexible overhead light source
Dissection equipment
Forceps (curved or straight)
Pointed fine forceps (curved or straight)
Fine scissors (for general dissection)
Micro scissors (for heart dissection)
Laboratory work station
In quiet, well ventilated room, specific for purpose
Adequate space for:
- manipulation of specimen under examination
- whole litter being examined
- labelled transfer containers, if appropriate, filled with appropriate fixative (if required)
- paper towels
- data collection system; paper records or monitor and keyboard
- Suitable chair
- Comfortable, safe
- 3 way adjustable
- Good overhead lighting
- Protective clothing
- Safety glasses
- Protective gloves
- Laboratory coat
- Access to reference material:
Terminology in Developmental Toxicology glossary
Company training guides, including recognition levels employed, Company SOPS, Examples of normal specimens
PREPARATION OF SPECIMENS
As fetuses are examined fresh there is no preparation required. Fetuses should be kept cool prior to examination and the time between death and examination kept as short as possible to prevent post mortem change complicating the interpretation of any findings.
If necessary, fetuses may be kept in a dilute alcohol solution to delay examination for up to 24 hours.
Following examination of the external surface of the fetus, a midline incision should be made from the genital papilla, up one side of the sternum, to underneath the lower jaw exposing tissues in the neck, thorax and abdomen. Following examination of the diaphragm this structure should be cut to facilitate further examination of the contents of the thoracic cavity. Care should be taken to avoid damage to tissues during the examination process. Blood vessels should be traced and their patency assessed. The internal structure of the heart and kidneys should be examined. The intestine should be checked for areas of constriction and blockage. The sex of the fetus should be assessed by examination of the gonads and should confirm that which was determined externally.
Learning objective: review the methods outlined by Stuckhardt and Poppe (1984) and Staples (1974). Compare and contrast these with the dissection method used in your laboratory.
ASSESSMENT OF NORMAL
It is considered important to remember that if the examination data are collected inaccurately, inconsistently, or with insufficient detail, meaningful interpretation of these data is impossible. The examination of fetal specimens is therefore a crucial step in the evaluation of reproductive toxicity studies. The importance of this stage in data evaluation cannot be overstated.
Recognition of the 'normal' appearance
Laboratory recognition levels are the cut-off points between what is considered to be 'normal' and what must be recorded as 'abnormal' within a particular laboratory over a particular time period. Also, where observations are qualified by estimates of extent ('severity'), recognition levels provide the cut-off points between severities (advice on the recording of severity is given below). Translated into practical terms, they are criteria enabling the examiner to make consistent decisions at the borderlines between different categories.
Between laboratories there can be differences in the recognition levels set for some observations. It would be difficult to attempt 'standardisation' across laboratories in this area, because this would require setting recognition levels at an unacceptably coarse level in order to allow for the many factors that lead to inconsistency (including strain of animal, time of necropsy, laboratory environment and procedures). The priority should be ensuring consistency within each laboratory, so that valid comparisons can be made between treated and control animals, both within and between studies conducted in that laboratory.
Deciding where to draw the line between what is considered unremarkable and what must be recorded as an observation is one of the most difficult problems in fetal examination. In all biological systems there is natural variation and very few individuals in a population, or in a population sample, will have a body conformation that complies precisely with any idealised textbook description (the anatomical norm or anatomical standard). Most individuals will have an appearance that differs slightly from the anatomical norm, but which does not do so sufficiently, nor so infrequently, as to be regarded as 'abnormal'. This range of conformity can be considered to constitute the population norm.
Each laboratory uses recognition levels in the recording of fetal abnormalities, which define the boundaries between what is considered to be normal and what is abnormal within that laboratory, and also in many cases the boundaries of the qualifications used to describe the extent of an abnormality.
Other considerations - Assessing mechanical damage
It is possible for mechanical damage to occur at necropsy e.g. subcutaneous haemorrhage.
It is strongly recommended that any damage known to have occurred during the stages before fetal examination is recorded and that appropriate notes are made available to the examiner. Where conditions observed at evaluation are suspected but not confirmed to be artefactual, evaluation requires a common-sense approach.
Other considerations - specimen quality
It is possible when the specimens are examined that all of the key structures are not clearly visible. If this is the case it is important to assess whether this is due to a true structural abnormality or to the quality of the specimen. To clarify this situation further dissection of the appropriate area should be performed.
Where clarification is required examples of questions to be considered are:
- Is there apparent asymmetry of bilateral structures?
- Do small structures appear to be absent?
- Do structures appear to be displaced?
- Do structures appear to be misshapen?
Click here to view the normal fresh rat fetus.
ASSESSMENT OF DIFFERENCES FROM NORMAL
Changes from normal should be recorded according to your own laboratory's standards, with references to internal recognition levels, using the appropriate SOPs, training guides, user manual and any other relevant training information.
'Severity' of observations
It is recommended that some means of categorising the degree of change or extent of an observation be devised to aid in interpretation. Commonly used systems use qualifiers such as minimal (or slight), moderate and marked (or severe). Defining these terms without specific examples is difficult, but the following general principles might be suitable:
- Minimal: Apparent at close scrutiny
- Moderate: Apparent without close scrutiny
- Marked: Strikingly obvious
Not all observations need to be qualified by severity, but where a single term might be descriptive of a wide range of severity (from a condition which is only slightly outside the normal range to one which is potentially much more harmful), a qualifier indicating severity is strongly recommended. Examples of such terms are: misshapen, displaced, enlarged, reduced in size, shortened and widened.
Where severities are used, they should be noted at the examination stage, but where appropriate they can be merged or rationalised at a later data evaluation stage. The data must be assessed carefully to ensure that such a rationalisation will not obscure or exaggerate any findings.
Learning objective: The Terminology in Developmental Toxicology glossary is an invaluable document. Review the visceral section and become familiar with the terms described.
LEARNING OUTCOME EXERCISES
Each of the thumbnails below will display an image taken during fresh examination. Lines point to some of the important structures. The pages have been sized so that you can print them, label the identified structures and then check your answers by pointing your mouse arrow at the end of each line.
Key learning point exercises and questions
Give 3 reasons why fresh examination is an effective method of examining rat fetuses externally/viscerally.
Name 3 requirements that should be in place in the lab before examination of fresh tissues can take place.
What protective clothing should you wear when performing examination of fresh tissues?
Where would you find a list of the head and body areas that should be looked at during external/visceral examination
Use your own specimens to find examples, if possible of:
Cleft palate
Subcutaneous haemorrhages
Absent/small thyroid gland
Any observations relating to the thymus gland
Any observations relating to the aortic arch/pulmonary trunk/ductus arteriosus.
Right subclavian artery arising from aortic arch (absent innominate artery)
Ventricular septal defects
What severity levels are they?
Are they relating to the membranous or muscular area of the septum?
Any observations relating to the lungs
Any observations relating to the diaphragm
Anomalous confluence of caudal vena cava with left hepatic vein
Any observations relating to the liver
Any observations relating to the kidney and ureter
What severity levels are they?
Any observations relating to the gonads
List 2 observations that may be associated with fetuses with subcutaneous oedema
List 3 observations, which would help you distinguish the abnormality situs inversus
REFERENCES
Barrow MV Taylor WY
A rapid method for detecting malformations in rat fetuses
J Morph 127 291-305 1969
Beck F
Evaluation of organs (gross organ pathology)
Methods in prenatal toxicology ed Neubert D Georg Thieme Stuttgart 1977
Ikemi N Otani Y Ikegami T Yasuda M
Palatal ruga anomaly induced by all-trans-retinoic acid in the Crj:SD rat: possible warning sign of teratogenicity
Reproductive Toxicology 15 87-93 2001
Olds RJ, Olds JR
A colour atlas of the rat � dissection guide
Wolfe medical publications Ltd
1979
Peters PWJ
Surface staining of Wilson razor blade slices
Methods in prenatal toxicology ed Neubert D Georg Thieme Stuttgart 1977
Rowett HGQ
Dissection guides IV the rabbit
John Murray 1952
Rowett HGQ
Dissection guides III the rat with notes on the Mouse
John Murray 1951
Stertz H, Lehmann H
A critical comparison of the freehand razorblade dissection method according to Wilson with an in situ sectioning method for rat fetuses
Tera Carc Mutag 5 347-354 1985
Van Julsingha EB, Bennett CB
A dissecting procedure for the detection of anomalies in the rabbit fetal head
Methods in prenatal toxicology ed Neubert D Georg Thieme Stuttgart 1977
Whitehouse RH Grove AJ
The dissection of the rabbit with an appendix on the rat
University tutorial press Ltd 1933
Wilson JG
Methods for administering agents and detecting malformations in experimental animals
Teratology Principles and Techniques 262 277 1965
Yasuda M Ohya R Sato TJ Inoue N
Variations in the palate rugae in the mouse as an indicator for detection of teratogenicity
J Toxicol Sci 17 348 1992
